#140 Physical Properties of Functional Plating
Physical properties of functional plating are as follows.
|
(1) Solderability
This is regarding how well solder bonds with two metal surfaces, and it describes solder affinity and the wetness of solder. This characteristic is indispensable to electronic, semiconductor, electrical and machine parts that require soldering.
(2) Bondability
| Connecting the electrodes of semiconductor devices to lead frames is called Bonding. Gold and aluminum wires are typically used for these connections, and how well the connections are made is called Bondability. The characteristics required for the plating are layer softness, surface cleanliness, heat adhesiveness. Gold, silver, electroless nickel platings are used. | 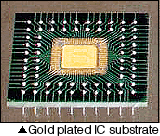 |
(3) Porosity
This is a characteristic of having many minute pores on surfaces where lubricants can be retained. Lubricity is extremely important for the pistons and cylinders of internal combustion engines, and porous industrial chrome satisfies that purpose.
(4) Non-adhesiveness
This means as same as mold releasing ability where objects do not adhere to things. This at the same time relates to low friction coefficient and sliding characteristics. Conventionally, mold releasing compounds were used on rubber and plastic molds in order to promote de-molding of workpieces, but application of dispersion plating with good non-adhesive characteristic enabled molding processes without the mold releasing compounds.
(5) Adhesiveness/Coating adhesiveness
This is a property to improve adhesion quality of metals and organic polymeric materials such as paints, linings, and composite material formations. With automotive radial tires, steel wires are dual layer plated with copper and zinc, then heat treated to be dispersed in order to improve the adhesion with rubber.
- Environmental conservation
- Hot Dipping
- Anodic Oxidation Process
- Anodic oxidation treatment
- Anodizing
- Corrosion - Corrosion Protection
- Electroless Plating
- Electroplating
- Heat treating
- Hydrogen embrittlement
- Metal cleaning
- Metal etching
- Painting
- Special paints
- Surface Treatment
- Surface-treated steel sheets
- Thermal Spraying



