#014 Moment of Inertia of of areaMold Components
The moment of inertia of areamold components which is important for forecasting bending is explained below.
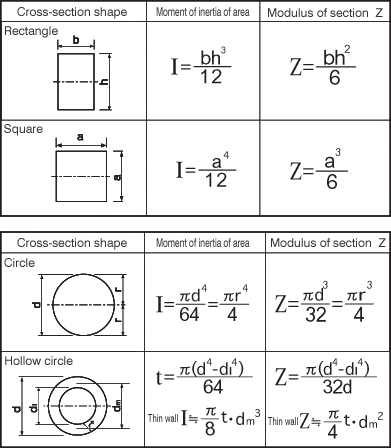
At the time of carrying out the strength calculations of a mold for plastic injection molding, the term "moment of inertia of area" appears very frequently. Let us understand again what "moment of inertia of area" is so that it is possible to progress while accurately understanding the calculation mechanics. Moment of inertia of areais a value that is identified by the cross-sectional shape of the part. This is used frequently for estimating the amount of deflection due to the bending moment or injection pressure. The moment of inertia of area changes depending only on the cross-sectional shape of a part. Therefore, it has no relationship with the material. For example, if the cross-sectional shape is the same, the value of the moment of inertia of area of areais the same whether the material is a non-heat treated steel, tempered steel, or even wood. The definition of moment of inertia of area according to mechanics is as follows. "When a cross-section is divided into an infinite number of differential areas dA and the distance from one axis X is a taken as Y, the moment of inertia of area is the sum over the entire area the product of the differential area and the square of the distance".
This can be expressed in the form of an equation as follows.
Cross-section second order moment is -
![]() (unit is mm4or m4)
(unit is mm4or m4)
The moment of inertia of aarea is usually represented by the symbol I as a matter of custom. In general, the strength against bending becomes larger as the moment of inertia of aarea becomes larger. If the cross-sectional shape is rectangular or circular, the basic equation for calculation becomes clear as is shown in Table 1.