#214 Heat-Saving Measures - Boiler Management -3
(3) Boiler combustion management
As explained in the previous session, boilers have to go through a pre-purge and a post-purge cycle before and after ignition in order to purge unburned gas from the furnace for safety purposes. During both of these purge cycles, the air blower feeds air to red-hot refractory materials in the furnace. Significant heat loss occurs during this cooling process.
[Fig.1] shows the boiler operating status surveyed at a plant. The figure below is a timeline showing the electric current consumption by a boiler.
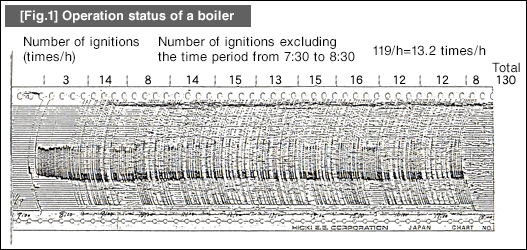
As is obvious from the figure, the number of ignitions per hour is three before commencing the daily operation, but has increased to 13 during the operation period on average, which is equivalent to approximately one ignition every five minutes.
[Fig.2] show the result of more detailed operation status by speeding up the electric current recorder.
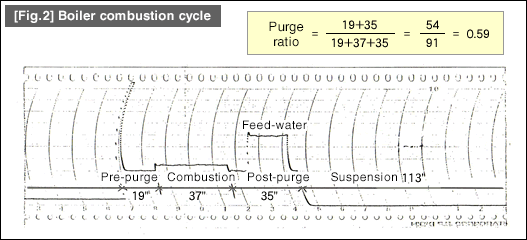
As we can see in the figure, the combustion period is 37 seconds while the purge period is 54 seconds in total, consisting of 19 seconds of pre-purge and 35 seconds of post-purge period. Based on this, the purge ratio is calculated as 54/(54+37) = 59%. This means that the period of cooling of the boiler is longer than the combustion period. In such situations, we are disposing of a large portion of fuel energy into the air. To address this inefficiency, it is necessary to reduce the number of ignitions as well as the purge period.
- Environmental conservation
- Hot Dipping
- Anodic Oxidation Process
- Anodic oxidation treatment
- Anodizing
- Corrosion - Corrosion Protection
- Electroless Plating
- Electroplating
- Heat treating
- Hydrogen embrittlement
- Metal cleaning
- Metal etching
- Painting
- Special paints
- Surface Treatment
- Surface-treated steel sheets
- Thermal Spraying



