HOME > Surface Finishing Tutorial > #236 Saving Water for Washing and Cleaning (by Ion Exchange) -2
Surface Finishing Tutorial
#236 Saving Water for Washing and Cleaning (by Ion Exchange) -2
Category : Environmental conservation
April22, 2016
There are various combinations of ion-exchange towers. [Fig.1] illustrates an example of towers assembled for purifying plating wastewater. This is probably a good example of learning the types of ions that can be adsorbed by each type of ion-exchange towers.
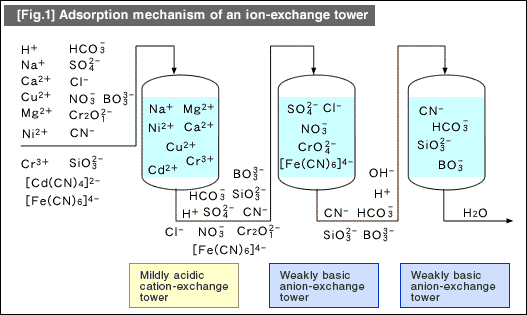
Based on these adsorption characteristics, ion-exchange towers are proven to be effective in the following usages:
| 1. | If you circulate water in the final rinse tank used for countercurrent multistage washing and adopt the ion-exchange method, it will eliminate fresh feed-water and drainage from the system. | |
| 2. | In the similar manner, if you use chelating resin that separates and adsorbs certain metals, the resin collects the certain metals from the eluting solution. (Examples of metals are gold, silver, platinum, nickel, copper, etc.) | |
| 3. | Use an ion-exchange tower to adsorb and eliminate metal of impurities in the plating solution collected by spray washing. By purifying the plating solution, you can extend the operating life and prevent aging or wasting of the plating solution. |
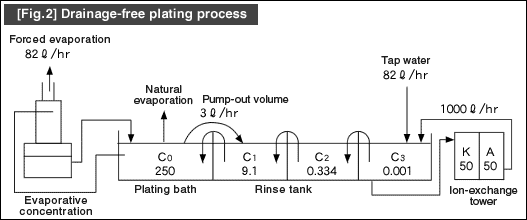
[Fig.2] illustrates an example of the rinsing water circulation system with an ion-exchanger assembled in the final rinse tank. This system uses the countercurrent multistage washing method along with the forced evaporation method for the plating solution.
- Environmental conservation
- Hot Dipping
- Anodic Oxidation Process
- Anodic oxidation treatment
- Anodizing
- Corrosion - Corrosion Protection
- Electroless Plating
- Electroplating
- Heat treating
- Hydrogen embrittlement
- Metal cleaning
- Metal etching
- Painting
- Special paints
- Surface Treatment
- Surface-treated steel sheets
- Thermal Spraying



