#208 Hot Dip Galvanizing -1
(1) Plating pretreatment process
| The figure shown below is the basic work process of hot dip galvanizing. To be brief, this process can be classified into the following three stages: 1) Pretreatment process to remove rust, scale, and oil content from the plating substrate surface; 2) Plating process to form a zinc film on the surface by immersing the substrate into molten zinc; 3) Finishing process to make the plated products conform to the required quality standard. |
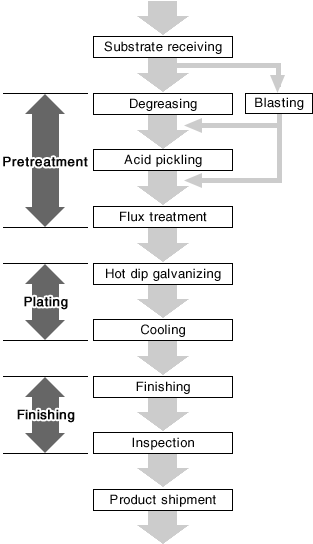 |
Wet processes such as alkaline degreasing are the common method in the batch treatment. On the other hand, continuous treatment such as hoop plating uses a method where the substrates pass through a furnace at 700 to 900℃ to perform annealing on steel materials as well.
Acid pickling is an important process to enhance the adhesiveness by forming an alloy layer between the zinc and the steel substrate after removing oxidized materials that have formed on the iron/steel products. Most commonly, sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid will be used in this process.
Blasting is a method of removing rust or scale by spraying abrasive grains or glass beads with high-pressure air. This method is applied to carbon steel and high-tensile steel that are likely to suffer from hydrogen embrittlement caused by acid pickling.The adhesiveness with the zinc coating is improved by shot blasting, grit blasting, and sand blasting as they roughen the surface.Therefore, blasting may be performed for the purpose of improving adhesiveness and increasing the adhesion amount.
The purpose of performing the flux treatment after acid pickling is to facilitate a reaction of steel and zinc on the product surface. This treatment also eliminates zinc oxide on the molten zinc surface immersed in a plating bath by removing adhered substances on the steel surface or small rust generated after acid pickling.
The flux treatment has the following two methods: 1) Dry method - the metal object is preheated and dried after being soaked into the heated 10% zinc chloride ammonium solution (or ammonium chloride); 2) Wet method - molten salt of zinc chloride ammonium is formed on the molten zinc of a plating bath, and the metal object is treated with the molten salt.

- Environmental conservation
- Hot Dipping
- Anodic Oxidation Process
- Anodic oxidation treatment
- Anodizing
- Corrosion - Corrosion Protection
- Electroless Plating
- Electroplating
- Heat treating
- Hydrogen embrittlement
- Metal cleaning
- Metal etching
- Painting
- Special paints
- Surface Treatment
- Surface-treated steel sheets
- Thermal Spraying



