#210 Hot Dip Galvanizing -3
(3) Cooling
Lift up the product from a zinc bath and allow excess molten zinc to drip off. Then, cool the product.There are two cooling methods available: water-cooling and air-cooling. In general, air-cooling is more commonly used.To prevent distortion caused by rapid cooling, use hot water at 70 °C or higher instead of cold water.Use air-cooling for thick plates to minimize distortion. However, air-cooling is known to degrade the appearance compared to water-cooling.
(4) Finishing
Finish the plated product by removing zinc drop on the product end, zinc residue and non-plating agent on the non-plating area, zinc accumulated in the pore, excessive roughness, etc.
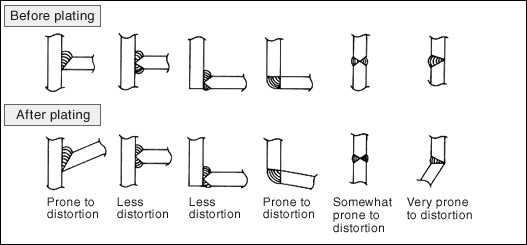
Residual stress that occurs during the production process of the steel products is released by plating heat, which causes distortion to appear on the product.From the commercial point of view, it is necessary to consider whether the degree of distortion is within the permissible limit and corrections are needed or feasible.The figure below is a specific example of distortion caused by welding methods.
(5) Partial non-plating
Some steel frame products require welding after the plating process. With such types of products, there are areas not to be plated.In this case, non-plating measures are necessary.As a non-plating measure, you can remove the plated area using a grinder. However, applying this method increases the cost.Another non-plating measure is to protect the non-plating area by masking.
Masking methods include the followings:
1.Masking using caustic lime or heat-resistant materials.
2.Acid pickling on the non-plating area after applying chemical-proof coating so that rust and scale remain on the material.
3.Perform Step 1 after Step 2.
* The next section explains the continuous manufacturing of surface-treated steel sheets in a mass production line.
- Environmental conservation
- Hot Dipping
- Anodic Oxidation Process
- Anodic oxidation treatment
- Anodizing
- Corrosion - Corrosion Protection
- Electroless Plating
- Electroplating
- Heat treating
- Hydrogen embrittlement
- Metal cleaning
- Metal etching
- Painting
- Special paints
- Surface Treatment
- Surface-treated steel sheets
- Thermal Spraying



