#224 Plating Thickness Measurement by Magnetic Method
(1) Measurement principle
Apply an alternating current to the probe with a winded coil around the iron core. Place this probe onto the sample surface. The plating thickness is determined by measuring changes in the magnetic resistance of the magnetic flux that runs through the plating surface and basis metal. Because this method uses lines of magnetic force, it is designed to measure the plating thickness of non-magnetic metal on magnetic basis metal.
In general, this method is used for measuring zinc plating, chrome plating, copper plating, tin plating, and solder plating on an iron and steel substrate.
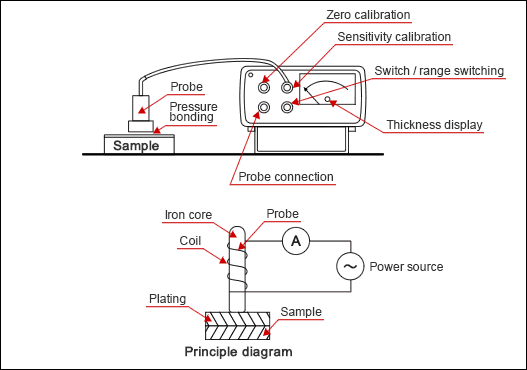
(2) Operation
| 1. | The basic operation is same as measurements by an eddy current. Prepare a substrate (made of the same materials) in the same shape as the plating sample (plate, round bar, pipe, etc.) as well as a standard sample with a known thickness. | |
| 2. | Keep the surface roughness consistent with that of the sample since it affects the measurement accuracy. | |
| 3. | Place the probe on the substrate. Then, set the indicator pointer to zero (zero calibration). | |
| 4. | Next, set the standard sample onto the substrate. Place the probe and calibrate the indicator pointer according to the standard sample thickness (sensitivity calibration). Repeat steps 3 and 4 three to four times. | |
| 5. | Measure the unknown sample under the same conditions that were applied to calibration. Measure the same area at least three times. Exclude any abnormal values and compute the average. |
(3) Precaution
Please note that the following factors are known to affect the measurement accuracy:
1. Plating thickness; 2. Magnetic property of basis metal; 3. Thickness and shape of basis metal; 4. Surface roughness; 5. Edge effect.
- Environmental conservation
- Hot Dipping
- Anodic Oxidation Process
- Anodic oxidation treatment
- Anodizing
- Corrosion - Corrosion Protection
- Electroless Plating
- Electroplating
- Heat treating
- Hydrogen embrittlement
- Metal cleaning
- Metal etching
- Painting
- Special paints
- Surface Treatment
- Surface-treated steel sheets
- Thermal Spraying



