#250 Metal Cleaning - Surfactant - 3
(5)Emulsification
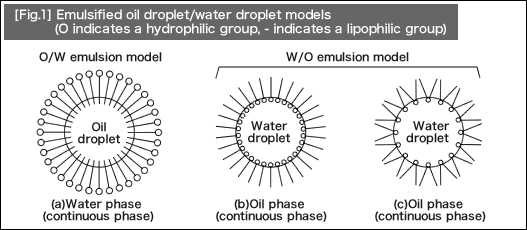
Surfactant solution emulsifies and disperses lipophilic dirt in a liquid form into fine and stable small drops. Molecules of the surfactant adsorb hydrophobic groups into an oil droplet. The product resulting upon this process is O/W (oil-in-water) emulsion. [Fig.1] (a) shows the image.
On the other hand, when a water droplet is emulsified in oil-based liquid, W/O (water-in-oil) emulsion will be formed. This type of emulsion is shown in [Fig.1] (b) and (c). In general, "emulsion" refers to the emulsified materials described here.
(6)Suspension
Solid fine particles will be also dispersed into water by adsorption of surfactants just like the emulsification. Since the surfactant molecules are simply adsorbed onto a solid surface in this case, they are less stable than emulsification.
(7)Foaming
Surfactant molecules have foaming properties. The cleaning effect is obtained when the foams adsorb dirt particles by wrapping them up on the surface.
However, excess foaming will cause various problems during the work process. To prevent excess foaming, select surfactants with lower foaming properties or use a silicone-based antifoamer.
(8)Solubilization
Solubilization is a phenomenon that a water-insoluble material is adsorbed or dissolved into surfactant micelles in a solution to produce clear liquid.
- Environmental conservation
- Hot Dipping
- Anodic Oxidation Process
- Anodic oxidation treatment
- Anodizing
- Corrosion - Corrosion Protection
- Electroless Plating
- Electroplating
- Heat treating
- Hydrogen embrittlement
- Metal cleaning
- Metal etching
- Painting
- Special paints
- Surface Treatment
- Surface-treated steel sheets
- Thermal Spraying



