#274 Heat-Saving Measures - Steam Properties -2
(2)Heat quantity of steam
Now, let's see how much heat energy the steam has. To find out, "steam tables" are useful.
Pressure-based and temperature-based steam tables are available. Values in both tables are expressed in absolute pressure (Mpa).
The table here is in the pressure-based format. Since a pressure gauge is used for displaying the pressure of ordinary steam boilers, [Table 1] lists the temperature and heat quantity based on the readings of a gauge pressure (MpaG).
[Table 1] Steam table
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note) | 0.1 MpaG = 1.0 Kg/cm2G (former display unit), KJ = 0.2389 KCaL, KCaL = 4.186 KJ |
In the above table,
gauge pressure is the steam pressure displayed on a pressure gauge. Specific enthalpy refers to the amount of heat for 1 kg of steam at the pressure displayed on the gauge.
It breaks down to sensible heat and latent heat. In this table, Total heat = sensible heat + latent heat. Sensible heat and total heat increase as the steam pressure becomes higher. However, latent heat decreases at this time.
As described in the previous volume, the heat circulates in the heating system of plating bath. See the figure below.
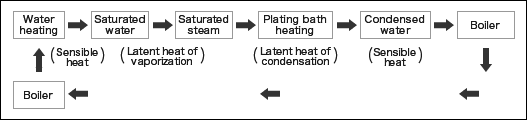
Indirect heating is a common method for heating plating bath in general, such as using a heater with corrugated tubes or a heat exchanger to circulate plating solution in a pump. Therefore, the latent heat of condensation of water is the only heat effectively used in this heating system.
Now, suppose you have used the steam with the gauge pressure 0.2 MpaG. In this table, the total heat is 2,725 KJ/kg for 1 Kg of steam, but the heat quantity available for heating the plating bath is only 2,163 KJ/kg.
- Environmental conservation
- Hot Dipping
- Anodic Oxidation Process
- Anodic oxidation treatment
- Anodizing
- Corrosion - Corrosion Protection
- Electroless Plating
- Electroplating
- Heat treating
- Hydrogen embrittlement
- Metal cleaning
- Metal etching
- Painting
- Special paints
- Surface Treatment
- Surface-treated steel sheets
- Thermal Spraying



