#083 LCA for Transfer - Gravity-Operated Feeder Systems
Gravity-operated feeder systems that require no drive mechanisms can be built inexpensively. This section outlines the principles and features of these feeder systems.
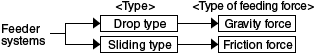
[Table 1] Features of gravity-operated feeder systems (chute type systems)
|
1. Descriptions
(1) Drop type
The distance (L) from storage hopper to workpiece holding carrier and the time (t) required for workpiece feeding can be determined using the following formula (See Fig. 1a):
t = √2L/g
g : Gravitational acceleration (mm/s2)
![[Fig. 1a] Gravity-operated feeder system (typical drop type) [Fig. 1a] Gravity-operated feeder system (typical drop type)](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/lca/images/087_02.gif)
The orientation of the workpiece can be kept unchanged while dropping using the characteristics of the shape of each workpiece and the position of the center of gravity.
(2) Sliding type
The feeding speed can be controlled using two design parameters: angle (θ) and friction coefficient (μ) of the slide chute (See Fig. 1b):
![[Fig. 1b] Gravity-operated feeder system (typical sliding type feeder and its design parameters) [Fig. 1b] Gravity-operated feeder system (typical sliding type feeder and its design parameters)](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/lca/images/087_03.gif)
The friction coefficient (μ) is adjustable to some degree using the contact area of the transferred workpiece with the sliding surface. Therefore, the sliding speed can be controlled via the chute sliding surface, which may consist of, e.g., punched plates. The time t required for feeding can be determined using the following formula:
t=√{2L/g (sinθ - μcosθ )}
L : Length of straight section of slide chute (mm)
g : Gravitational acceleration (mm/s2)
θ : Tilt angle
μ : Friction coefficient
(Mild steel : 0.40, cast iron : 0.20, aluminum : 0.36)
If equipped with a vibrational parts feeder, a sliding type feeder system is capable of aligned feeding of workpieces with complicated shapes. This section assumes the use of simplistic jigs, such as auxiliary jigs, for use in one-piece flow production lines.
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



