#034 Motion Mechanism Design - 4 : Stepper Motor
Electrical actuators that can be motion controlled with sequence programs are suitable for positioning applications and multiple variety production systems. There are motors with direction reversing capability, with brakes, and torque detection capability. Here, easy to control stepper motors suitable for LCA(Low Cost Automation) applications will be discussed.
(1) What is a stepper motor?
A stepper motor is a motor where its rotation (rotation angle/speed) is controlled by advancing or retarding the motor's built-in primary step angle with externally controlled number of pulses and frequency. In a case for 5-phase stepper motor system, the motor's built-in primary step angle is 0.72 degrees/step (360 / 500 pulses). In order to rotate a 5-phase motor 90 degrees, 125 steps will need to be programmed. Under no load condition, a step accuracy is 0.05 degrees and this high accuracy is not step to step cumulative.
(2) Stepper motor system configuration
A system configuration comprised of: PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) + Stepper motor controller + Stepper motor driver + Stepper motor is needed to control the rotation of a stepper motor (see [Fig.1]).
![[Fig.1] Basic stepper motor system configuration](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/lca/images/034_1.gif)
Programs in the PLC are converted into pulse signals (see [Fig.2]) in the controller, then converted into motor controlling electrical current in the driver.
![[Fig.2] Pulse signals](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/lca/images/034_2.gif)
(3) Motion controlling method
Rotation angle and speed are calculated by the following equations.
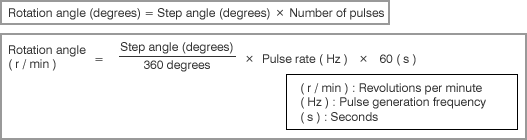
Example
Case for: Step angle:0.72 deg., Pulse rate: 100Hz... 12(r/min)・・・ 12 rotations per minute Case for: Step angle:0.72 deg., Pulse rate: 1000Hz... 120(r/min)・・・ 120 revolutions per minute
(4) About "Origin position" (home position)
Since the stepper motors do not have own rotation angle references, mechanical home positions must be provided when used for LCA positioning applications.
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



