#120 Production Technology Improvement Course for Mechanical Designers - 4: Key Considerations for Automation Design for Insertion Assembly - 3
When designing the gripped portions of parts to be inserted using automated insertion equipment, the characteristics of the parts' shapes and the force created during insertion (leading to, for example, deformation due to insertion counterforce) must be taken into account.
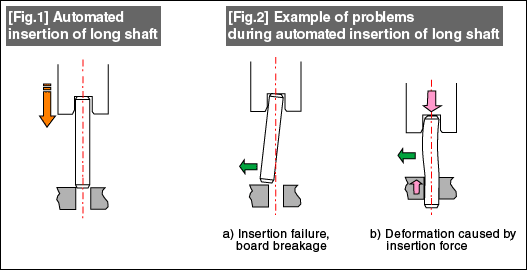
(1)Example: Automatic insertion of a long shaft
- If automatically inserting a locating or rotary shaft into a circuit board or plastic board (Fig. 1), the inserted shaft can be fixed in place without the use of adhesive or similar material by using the elastic deformation force of the insertion hole.
- When performing this type of insertion, errors during automatic insertion can result in troublesome process faults such as board breakage and reclamation difficulties.
- Elastic deformation from a board at insertion generates an unexpectedly complex counterforce. Stick slip causes problems such as intermittent repulsive force and rotating torsion. It is important to use gripping mechanisms that minimize the effects of these types of fluctuations (Fig. 3).

- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



