#169 Production Technology Level-up Course For Machine Designers - 5: Swaging Technology - Swaging Types - 1
Generally, products are composed of multiple parts functionally combined into assembled products. In this assembly process, the key points are product designs and assembly production techniques that are economical and contributes in stable quality. Furthermore, in environmental perspective, product nature that does not require disposal costs are desired. From here, one of the representative assembly elemental technology "Swaging" is explained.
(1) What is Swaging Technology
| ・ | Parts fastening procedures include: (1) Screw fastening, (2) Adhesive bonding, (4) Welding, (5) Swaging, etc. |
| ・ | The swaging technique is a procedure to permanently fasten parts by deforming the connection points of the parts. |
| ・ | Swaged states can be classified in two following types, a) Solid connection of parts [Photo 1] [Photo 2], b) Connection of parts where parts can rotate in relation to each other [Photo 3]. |
![[Photo 1] Swaging example of solid connection of parts [Photo 1] Swaging example of solid connection of parts](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/lca/images/169_1.gif)
![[Photo 2] Swaging example of magnetic head [Photo 2] Swaging example of magnetic head](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/lca/images/169_2.gif)
![[Photo 3] Swaging example where swaged parts can rotate [Photo 3] Swaging example where swaged parts can rotate](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/lca/images/169_3.gif)
(2) Characteristics of Swaging Technology
| 1.Advantages | ・By the use of fixtures and automated equipment, firmly bonded assembly is possible in short time. ・Reliable and easy to automate process. ・Design quality of swage section largely affects the process. |
| 2.Disadvantages | ・Investments are required such as fixtures and automation equipment. ・Since post-swaging disassembly is typically not possible, appropriate selection where the procedure is applied. |
Types and characteristics of swaging will be explained. Source of the figures is Assembly Elemental Technology Manual issued by Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun, Ltd.
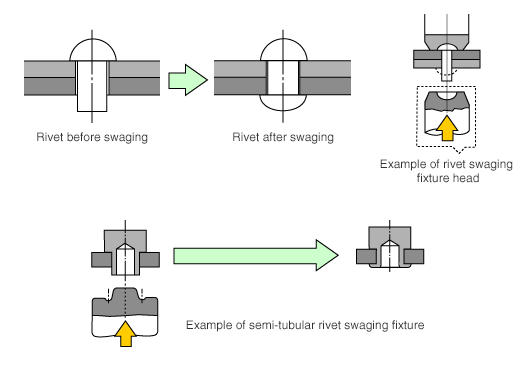
1) Rivet connection
Through holes are made on 2 plate material, and a rivet with smaller O.D. than the hole is inserted and both ends of the rivet are crushed to connect the parts.
![[Photo 1] Swaging example of hard disc head and arm [Photo 1] Swaging example of hard disc head and arm](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/lca/images/169_5.gif)
[Photo 1] Swaging example of hard disc head and arm
Description: Stainless steel head mount rivet is inserted into a hole on a convex/concave formed aluminum arm, then a steel ball is passed through the hole to quickly swage.
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



