#240 Mechanical Engineering and Automation Device Design - 6: Equilibrium of Forces
When the object is motionless even with two or more forces applied on the object, these forces are in an equilibrium state.
(1) Equilibrium of forces applied on a single point
- For a tug of war, the rope position does not move when this rope is being pulled towards opposite directions at the same strength of forces. This is an equilibrium state of forces (See the below figure).
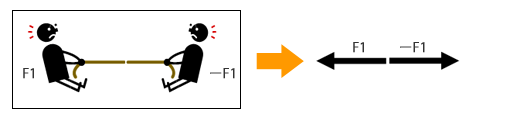
- When the resultant forces are the same in opposite directions, it will create an equilibrium of forces even though the forces are not applied on the same line.
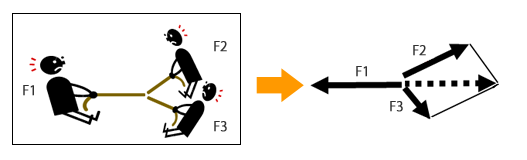
- When a force is applied from the opposite direction of the resultant force, forming a triangle of forces, these forces are in an equilibrium state. In this case, the polygon of forces is closed in the same direction (see the right image shown below).
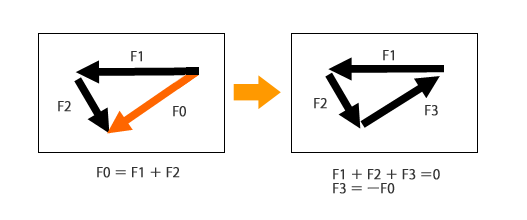
(2) Case example of force equilibrium in mechanical equipment
- For high-speed and high-precision motion control of a heavy movable body, the mechanism with equilibrium of forces applied may be incorporated into the design in order to reduce the load burden on the movable body.
- For the vertical drive control mechanism in particular, keep the forces in equilibrium by adding a spring (see the images below), an air cylinder, or a pulley on one side and placing a weight on the other side.
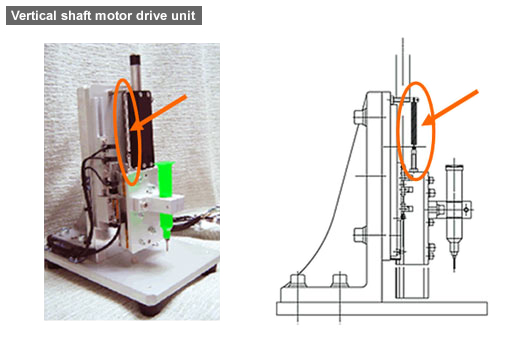
In order to bring out the high-speed drive performance of a linear motor (shaft motor), the spring suspension structure has been adopted for weight reduction of the vertical movable body.
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



