#241 Mechanical Engineering and Automation Device Design - 7: Conditions for Equilibrium of Forces
In this volume, we will learn about the equilibrium of forces when forces apply onto an object at different points of application.
(1)Equilibrium of forces when forces apply at different points of application
- When the forces are applied to a disk at four different points of application as shown in the below figure, you can predict that this disk will rotate in a counterclockwise direction. Therefore, the forces applied to this disk are not in an equilibrium state.
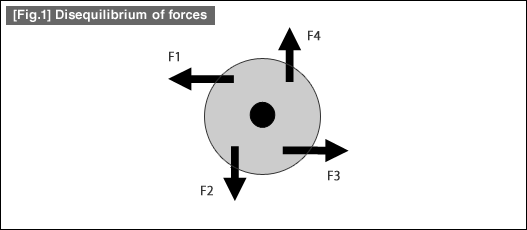
- If forces in different directions are applied at the same points of application as those shown above, the disk stops rotating and enters into a resting state. In this case, the forces applied at different points of application are in an equilibrium state.
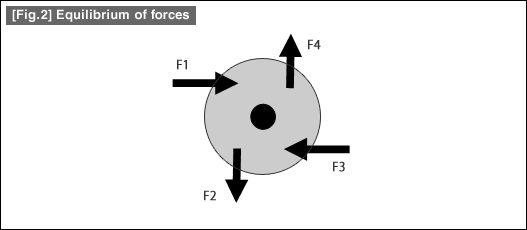
(2)Equilibrium conditions for forces from different point of application
The forces are in an equilibrium state when the following conditions are met for forces from different point of application.
a)The resultant force (Fi) of all forces becomes zero.
|
b)The sum of moments of these forces (Mi) applied to an arbitrary point becomes zero.
|
In the case of [Fig.2],
For a) : The resultant force of F1 and F3 is zero. The resultant force of F2 and F4 is also zero.
|
For b) : F1 and F3 have the same arm of moment in the opposite directions. Therefore, the moment is in an equilibrium state.
|
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



