#236 Mechanical Engineering and Automation Device Design - 2: Composition and Resolution of Forces - 1
In addition to the mechanical component that does the work, the entire structure is affected by force transmission and durability for all mechanical devices. In this volume, we will learn about the concept of force transmission from the relationship of "composition and resolution of forces".
(1) Composition of forces
In general, multiple forces are applied to a mechanical component. The effect of these forces combined can be expressed as the single force. The combined force here is called a "resultant force".
a) Resultant force of two forces along the crossing lines of action
As shown in the below figure, the resultant force can be explained by to which direction and how much force being applied to the ball when two forces F1 and F2 (in different direction and magnitude) are applied to the ball.
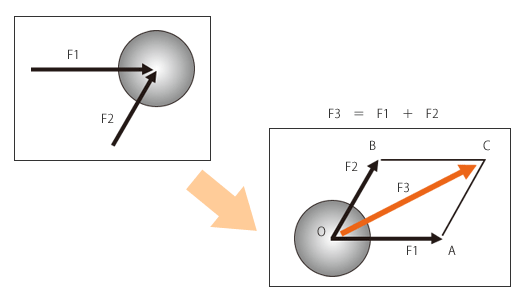
= How to compute the resultant force of two forces =
- Draw a parallelogram consisting of the two sides F1 and F2.
The parallelogram OABC in the right figure is called "parallelogram of forces".
- Of the two diagonal lines of this parallelogram, the diagonal line directing to OC (direction of force) drawn from the same point of application of F1 and F2 and the length (magnitude of force) represent the resultant force (force composition) of the two forces F1 and F2.
- Therefore, the ball moves in the orange arrow direction (F3) at the force ratio represented by the length of the arrow.
- As a case example of analyzing resultant forces, we prepared these graphic illustrations of the press machines with servomechanisms applied.
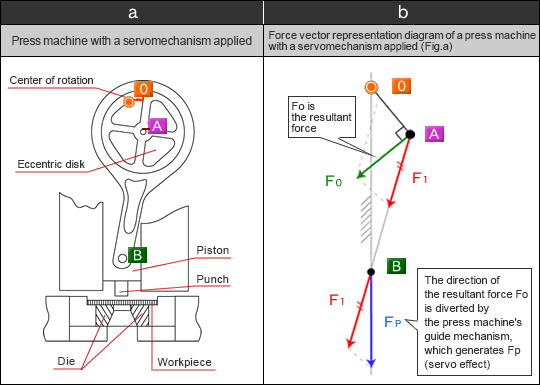
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



