#237 Mechanical Engineering and Automation Device Design - 3: Composition and Resolution of Forces - 2
b) Resultant force of more than two forces
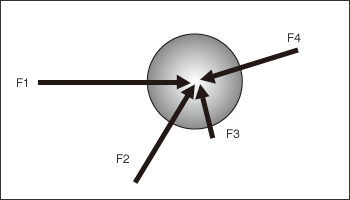
- In this section, we will learn about the composition of multiple forces on the same planar surface that are being applied to a center point of the ball.
- In the above figure, four different forces (vectors) F1, F2, F3, and F4 are applied to the center of the ball O.
- In this case, the resultant force is represented by an arrow of the last side (F5) of a polygon connected by four vectors.
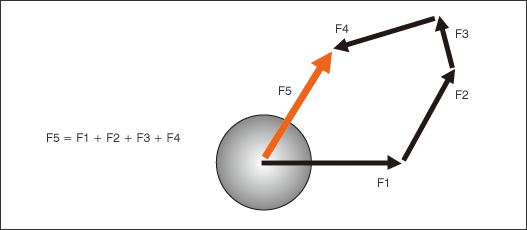
= Description =
- In the previous volume, we learned that the diagonal line for the parallelogram of forces represents the resultant force of two forces.
- The same result can be obtained by analyzing a triangle of forces in geometric configuration.
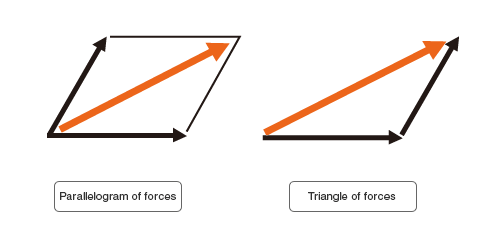
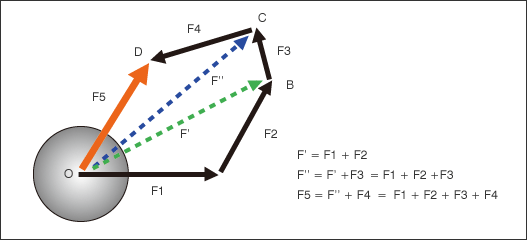
- It is possible to compute the resultant force of multiple forces by using this triangle of forces for the analysis.
- Even when multiple forces are applied to the ball, you can calculate the direction and magnitude (F5) of the ball's movement using the resultant force.
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



