#247 Mechanical Engineering and Automation Device Design - 13: Law of Motion - 3
In this volume, we will learn about the third law of motion: law of action and reaction.
(1)Law of motion
3)Newton's third law --- sometimes referred to as the action-reaction law.
- If one object A exerts a force on another object B, then B simultaneously exerts a force on A. The two forces here are equal in size and opposite in direction.
- When a ship A pushes another ship B, the both ships will be pushed against each other by the same magnitude of force in the opposite direction.
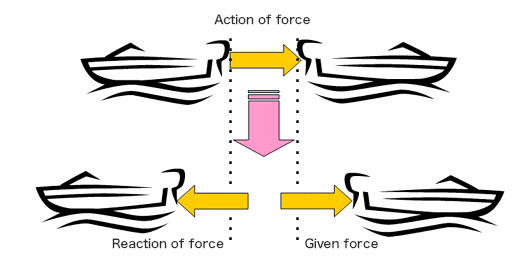
- Since we usually take this kind of reaction for granted, you may have a hard time understanding the concept, but you can really feel the reaction force at a sudden start while riding in the vehicle with a large acceleration.
- The action of force that you are pushed back against your seat is the vehicle's reaction force toward the moving force.
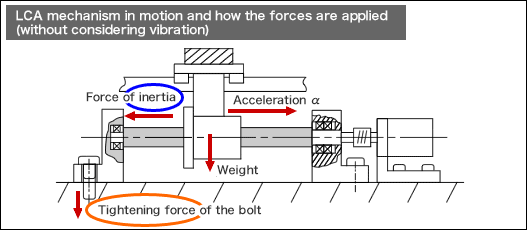
- This reaction force is a required strength value for support structures of the drive mechanism.
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



