#275 Spring Design -3: Load-Deflection Relationship for Helical Compression Springs
(1)Load-deformation relationship
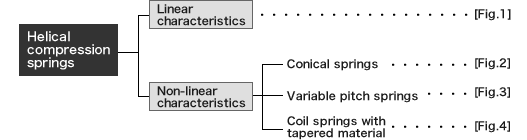
When the load on the spring: P and the deformation: δ are proportional to each other (in a linear relation), they are said to behave under "Hooke's law". The constant of proportion: k at this time is called the "spring constant". [Fig.1] shows a relationship between the load and deformation. The slope in this figure represents spring constant: k.
|
Examples of products designed and manufactured by taking advantage of this property include spring balances (scales for load weight measurement) and springs for safety valves operating at a certain required force.
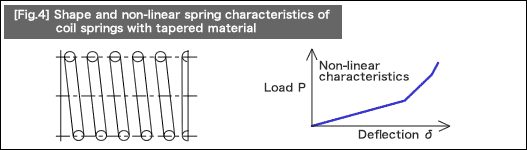
(2)Springs with various loading characteristics
Contrary to the linear characteristics shown in (1), some of the springs' load and deformation are in a non-linear relationship.
Helical compression springs having non-linear characteristics of load and deflection are available in the following three types:
The functions of helical compression springs with non-linear characteristics are achieved when the line or lines and the seating surface contact each other as the load increases. This occurs because the coil spring position causes a change in at least one of the following design parameters: [1] coil diameter, [2] pitch, or [3] wire diameter.
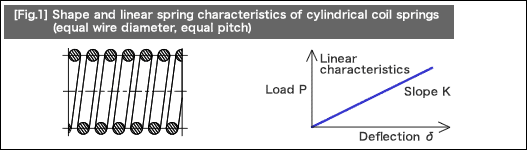
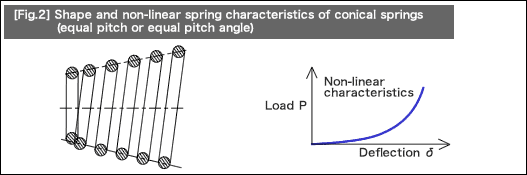
The following table summarizes advantages and disadvantages of typical springs having the non-linear characteristics introduced earlier.
= Advantages and disadvantages of typical springs with non-linear characteristics
|
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



