#215 Design Image Training - 31: Designing Reliable Automation Device
An automation device is comprised of the mechanism unit and drive unit with many components assembled along with other units including sensing/control units. This section explains the reliable design of an automation device that has a complex structure as described above.
- "Reliability" is a technical term defined in the JIS glossary. It is defined as "a characteristic of a system, device, or component thereof expressed as a probability that it will perform its required function under the given conditions within the specified operating periods".
-
"Reliability" is expressed by a multiplication formula (series model) of the reliability of all the assembly components comprising the automation device.
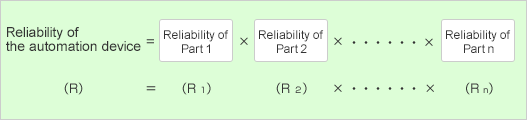
-
Since the reliability decreases by the number of components multiplied, it is more effective to decrease the number of components than to increase the reliability of individual component.
Examples:
* The reliability of the automation device with 10 components (90% reliability) assembled is R = 0.910 = 0.35, which is extremely low.
* Improving the reliability of 10 components to 93%: R = 0.9310 = 0.48
* Decreasing the number of components to eight by eliminating two components: R = 0.98 = 0.43
* Even if the reliability of each component is 99.9%, the overall reliability will be calculated as R = 0.9991000 = 0.368 for 1,000 pieces.
* For the system design requiring 100% reliability, such as a space satellite, the parallel model will be adopted instead of the series model for its redundancy. -
The table below shows the major failure factors for the assembly mechanism unit and sensing/control units (◎ indicates an extremely high ratio)
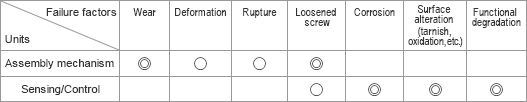
- As you can see from the above table, minimizing the number of components, especially the sensor components, is the important factor in designing a highly-reliable automation device.
- It is also important to adopt a design that is highly reliable and easy to maintain ("good accessibility" in other words) during the operating period.
- Positioning technology
- Designing and processing
- Sensor Technology
- Automation elements technology
- Clean room technology
- Design hints
- Design tips
- Designing and Machining
- Drive mechanism design
- Hints on designing
- Linear Motion Components
- Locating Technology
- Manufacturing technology
- Motion mechanism design
- Pneumatic Drives
- Production Technology
- Technology Outlook
- General description
- Low-cost automation and materials
- Transfer LCA
- #333 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 5: Multilayer pressurized heating process technique
- #332 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 4: Points to remember when designing mechanism of pneumatic pressurization method
- #331 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 3: Pneumatic pressurization method and pressure profile
- #330 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology - 2: Pressurization method and pressure profile
- #329 Know-how on automation: Pressurized heating technology



