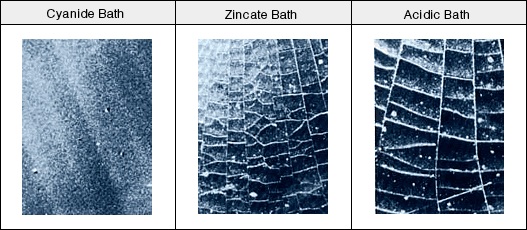
There are following two zinc alloy plating types being put to practical use.
(1) Zinc-Nickel Alloy Plating
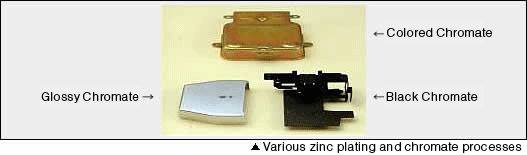
This is an anti-corrosive plating for products used in harsh corrosive environments able to cope with heavy environmental loads where the coating film thickness would have to be considerable if it were the conventional zinc plating. It has established its position as a type of plating of highly anti-corrosive and thin plating film thickness. Normally, it contains 5~10% nickel, and colored chromate processed specimen is highly anti-corrosive where it can withstand 2000 hours or more of salt water spray test without showing red rust. Additionally, it has good heat resistance characteristics and good post heat treatment corrosion resistance property and secondary workability. In addition, since this plating does not cause hydrogen embrittlement, it is possible to apply highly corrosion resistant plating on carbon steels and alloy steels, occupying important positions such as on functional parts of automobiles and etc. Colored and Brown chromate treatments are implemented for this plating.
(2) Zinc-Iron Alloy Plating
This is a plating of 5µm coating thickness, and has high corrosion resistance of 2000 hours or more of salt water spray test result. The coating film contains 0.2~0.7% of Iron, but it said to show the highest corrosion resistance property when the Iron content is 0.4%. Especially, the Black Chromate treatment has better corrosion resistance properties and more economical compared to the other zinc plating types. Also, the plating has good plating coverage characteristics as well as electro-deposition characteristics. There are: Glossy, Colored, Black Chromate treatments available, with the Black Chromate being the most popular in demand.

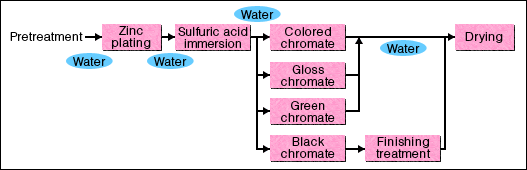
| ※ | Chromate Treatment When zinc and cadmium plated objects are submerged in solutions containing chromic acid and dichromate salt, the plate coatings are partially dissolved and chemically complex films are formed on the surfaces. When these are stabilized and dried, chromate coatings are formed. The formulation of these films greatly increase the corrosion resistance characteristics. However lately, popularity of Chromium-free movements are causing transitions toward chromate processes that do not use the chromium. |