(1) Load rate and thermal efficiency of a boiler
The thermal efficiency of a boiler is defined as the percentage of heat energy obtained from fuel that is effectively utilized to generate steam.
The thermal energy possessed by various types of fuel can be calculated from its chemical composition. The actual measurement values are also available from the suppliers.The fuel usage can be determined by an oil gauge or a gas flowmeter.
However, it is quite difficult to measure the amount of steam generated.It may be easier for big corporations as they usually have a steam flowmeter, but it is not the case for most small and mid-sized companies.For those without a steam flowmeter, it is still possible to estimate thermal efficiency using the amount of water supplied instead of the amount of steam generated.In this case, it is not an easy task to calculate the precise thermal efficiency because the thermal energy of steam generated varies according to the steam pressure.
To make this task simpler, calculate the evaporation ratio, which is the amount of water supplied (amount of steam generated) in kg per kilogram of fuel based on the fuel usage amount and the amount of water supplied (excluding the discharge amount) for a month.Use the steam table to calculate the thermal energy of steam based on the pressure (gauge pressure) of a boiler under normal operation. Then, calculate the thermal energy of the water supply at the feed-water temperature along with the thermal energy of fuel before combustion takes place. The approximate thermal efficiency can be calculated by using these values.
As the feed-water temperature and the fuel temperature vary season to season, these values fall within a certain range of the seasonal variation coefficient.
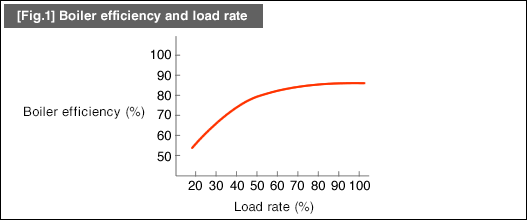
Recent boilers are more efficient than the conventional ones. You may see "thermal efficiency 98%" in the product catalog. However, this efficiency value can only be achieved at the optimum operating state during continuous operation.Such efficiency cannot be achieved during actual operation.This is because the load rate of a boiler fluctuates depending on the operating condition.
For example, when a surface treatment plant starts its operation, steam needs to be supplied continually to heat a degreasing bath or a plating bath. Once the bath temperature has risen to a certain temperature, the bath no longer needs that much steam since the high specific heat of these solutions minimizes the temperature drop.
In this case, the boiler operates at an extremely high efficiency with the load rate of 100% around the time of starting daily operations. Once the surface treatment work enters into a steady operation cycle, the boiler operates at low load with decreased efficiency as the burner intermittently burns fuel.In other words, the boiler releases more heat into exhaust gas during low-load operations.
[Fig.1] shows the relationship between the efficiency and load rate of a boiler.