| Base metal | Plating type,thickness | Applicationenvironment | Neutral salt waterspray test | CASS test |
| Steel | Cu+Ni10b,Cu+Ni15b,Cu+Ni20b | DNormal Interior, Residential home, Office, etc. | 24 | |
| NickelNickel alloy | Ni3b,Ni5b,Ni10b |
| Steel | Cu+Ni3b,Cr 0.1,Ni3b,Cr 0.1,Cu+Ni5b,Cr 0.1,Ni5b,Cr 0.1,Cu+Ni10b,Cr 0.1,Ni10b,Cr 0.1 | | 4 |
| Cu+Ni5b,Cr 0.1,Ni5b、Cr 0.1,Cu+Ni25b,Cr 0.1,Ni20b,Cr 0.1 | CHumid room | | 8 |
| Cu+Ni30b,Cr 0.1,Ni25d,Cr 0.1,Ni30b,Cr 0.1,Ni40b,Cr 0.1 | BNormal outdoor | | 16 |
| Cu+Ni50b,Cr 0.1,Ni30d,Cr 0.1mp | ACorrosive outdoor | | 24 |
| Copper,Copper alloy | Ni2b、Cr 0.1 | D | | 4 |
| Ni2b,Cr 0.1,Ni5b,Cr 0.1 | C | | 8 |
| Ni10b,Cr 0.1,Ni25b,Cr 0.1 | B | | 16 |
| Ni25b,Cr 0.1mp | A | | 24 |
| Zinc alloy | Cu+Ni10b,Cr 0.1,Cu+Ni15b,Cr 0.1 | D | | 4 |
| Cu+Ni20b,Cr 0.1,Cu+Ni25b,Cr 0.1 | C | | 8 |
| Cu+Ni30b,Cr 0.1,Cu+Ni40b,Cr 0.1,Cu+Ni30b,Cr 0.1mp,Cu+Ni40b,Cr 0.1mp | B | | 16 |
| Cu+Ni40b,Cr 0.1mp | A | | 24 |
| Aluminumand its alloys | Ni10b,Cr 0.1 | D | | 4 |
| Ni20b,Cr 0.1 | C | | 8 |
| Ni30b,Cr 0.1 | B | | 16 |
| Ni35d,Cr 0.1mp | A | | 24 |
|
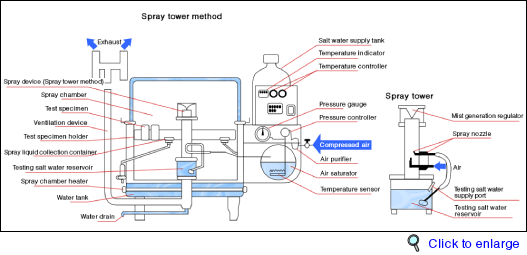
![[Fig.1]](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/surface/images/156_01.gif)
![[Fig.2]](http://www.misumi-techcentral.com/tt/en/surface/images/156_02.gif)