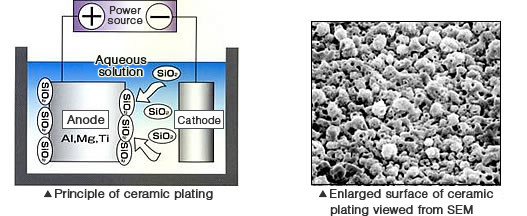
Technologies used for forming ceramic films on metal substrates include plasma spraying and PVD. This ceramic plating is classified as a form of wet plating and a technology where the ceramics are electrocrystalized and sintered on a metal substrate. Using the term "plating" for this method could be a little awkward. However, since the principle of forming ceramic films on the anode metal by energizing it in the aqueous solution is similar to that of electroplating, it is referred to as "ceramic plating".
Metals that are compatible with this plating method are those that can form passive films by being energized in the electrolyte, such as aluminum, magnesium, and titanium. To be able to use them for plating, these metals must be anodized.
Using silicate salt for the electrolyte solution is another important factor to remember. The anode surface becomes passivated by the electrolysis, followed by electrification and plasma discharge. The silicate attracted on the anode will be sintered and then turned into ceramic.
Adhesion properties of the deposited films are excellent. In addition, the films are superior in heat resistance and rated well on corrosion resistance. Since the films can be colored while they are resistant to bending and work well with the post-processing, ceramic plating is adopted for various applications, from decorative items such as high-end wall materials, kitchen items to functional applications including the products utilizing characteristics as far-infrared properties, resistance to ultraviolet rays and radiation, and vacuum-proof properties. It is estimated that the film can be deposited for up to 50 um.