According to JIS, the electroplating and electroless plating specifications must be indicated in the following classifications and orders:
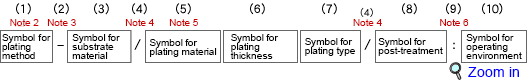
(1)Note 2) Symbol for plating method
EP: Electroplating, ELP: Electroless plating
(2)Note 3) Hyphen
(3)Symbol for substrate material
Fe: Steel, Cu: Copper and Copper Alloy, Zn: Zinc Alloy, AL: Aluminum and Aluminum Alloy, Mg: Magnesium Alloy, PL: Plastics, CE: Ceramics
(4)Note 4) Slash
(5)Symbol for plating material
Ni: Nickel, Cr: Chrome, Cu: Copper, Zn: Zinc, Au: Gold, Ag: Silver, Sn: Tin, Crr: Regular Chrome, ICr: Industrial Chrome
| Note 5) | For multilayer plating, the plating material compositions are specified from left to right, in the order closest to the substrate, and are separated with a comma.If both electroplating and electroless plating were used, the corresponding symbol followed by a hyphen is added before the plating material symbol.
Example 4 in the previous volume) EP-Fe/ELP-Ni 15, ICr 20 |
(6)Symbol for plating thickness
The unit is um (micrometer). e.g. 0.1, 5, 10, 20, 40
(7)Symbol for plating type
b: Bright plating, s: Semi-bright plating, d: Duplex plating, t: Three-layer plating, v: Fine matte plating, n: Non-smooth plating, m: Dull plating, cp: Composite plating, bk: Black plating, r: Regular plating, mp: Microporous plating, mc: Microcracked plating, cf: Crack-free plating
(8)Symbol for post-treatment
CM1: Bright chromate, CM2: Colored chromate, HB: hydrogen-removal baking, DH: Diffusion treatment, PA: Painting, CL: Coloring, AT: Anti-tarnish treatment
(9)Note 6) Colon
(10)Symbol for operating environment
A:Highly corrosive outdoor environment (e.g. coastal areas and industrial zones)
B:Normal outdoor environment (e.g. rural zones and residential areas)
C:Highly humid indoor environment (e.g. bathrooms and kitchens)
D:Normal indoor environment (e.g. inside of houses and offices)