(1) Single layer plating
Anti corrosion platings are mostly of single layer. Zinc and zinc alloy platings are widely used, for an obvious reason based on sacrificial anti-corrosion principle where metals such as zinc, etc. with high ionizing tendency need to be directly connected with the metals with low ionizing tendency. In recent years, Chromate treatment is being applied as a post plating process in order to further enhance the corrosion resistance of anti-corrosive platings. For instance, it prevents white rust on zinc plating. In addition, functional platings such as hard chrome (industrial) and copper plating for printing rolls are also of single layer. The reason is because only plating layer with a required specific property is needed.
(2) Multilayer platings
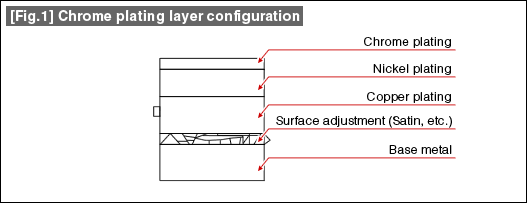
| Ornamental platings with corrosion resistance required are mostly of multilayer. The term ornamental plating can encompass a various characteristic requirements based on intended applications. For instance, chrome plating is applied on bicycle handlebars. The topmost plating layer is chrome plating for good wear resistance, and for the layer below, a nickel plating with good corrosion resistance and relatively high hardness is applied for beautiful handlebars that are hard to scratch and rust. Additionally, lead alloy rubber casting and zinc diecast bases are used to for jewelry, such as brooches for the ease of modeling where copper plating with good adhesion characteristic with zinc and lead alloy is first applied, then a nickel plating is applied for corrosion resistance. On the topmost layer, gold, platinum or rhodium plating is applied for increased product value. As explained, the ornamental platings are made multilayer with a various metals to satisfy the required product characteristics. It is possible to omit the nickel plating and use a thick layer of copper plating in order to reduce the cost, though if a gold plating is on top of the copper, the gold plating layer will diffuse onto the copper below and will be lost. As such, diffusion and permeation occur with some combinations of metals and countermeasures are required for the multilayer plating designs. |  |
As seen above, the plate layer designs are determined based on product application environments, required characteristics, metal properties, and cost structure.